13 Pruebas de independencia de los errores
En este capítulo se presentan varias pruebas para explorar si se cumple el supuesto de independencia de los errores en regresión lineal.
En las prueba mostradas a continuación se estudian las siguientes hipótesis.
\[\begin{align*} H_0 &: \text{los errores son independientes.} \\ H_1 &: \text{los errores no son independientes.} \end{align*}\]
Durbin-Watson test
La función dwtest del paquete lmtest (Hothorn et al. 2022) implementa esta prueba.
En esta publicación de StackOverFlow hay una excelente discusión sobre la prueba, se invita al lector a explorar la publicación.
Ejemplo
El siguiente ejemplo fue tomado de la documentación de la función dwtest.
## generate regressor
x <- rep(c(-1, 1), 50)
## generate the AR(1) error terms with parameter rho = 0 (white noise)
err1 <- rnorm(100)
## generate dependent variable
y1 <- 1 + x + err1
library(lmtest)
mod1 <- lm(y1 ~ x)
dwtest(mod1) ## perform Durbin-Watson test##
## Durbin-Watson test
##
## data: mod1
## DW = 2.0407, p-value = 0.6204
## alternative hypothesis: true autocorrelation is greater than 0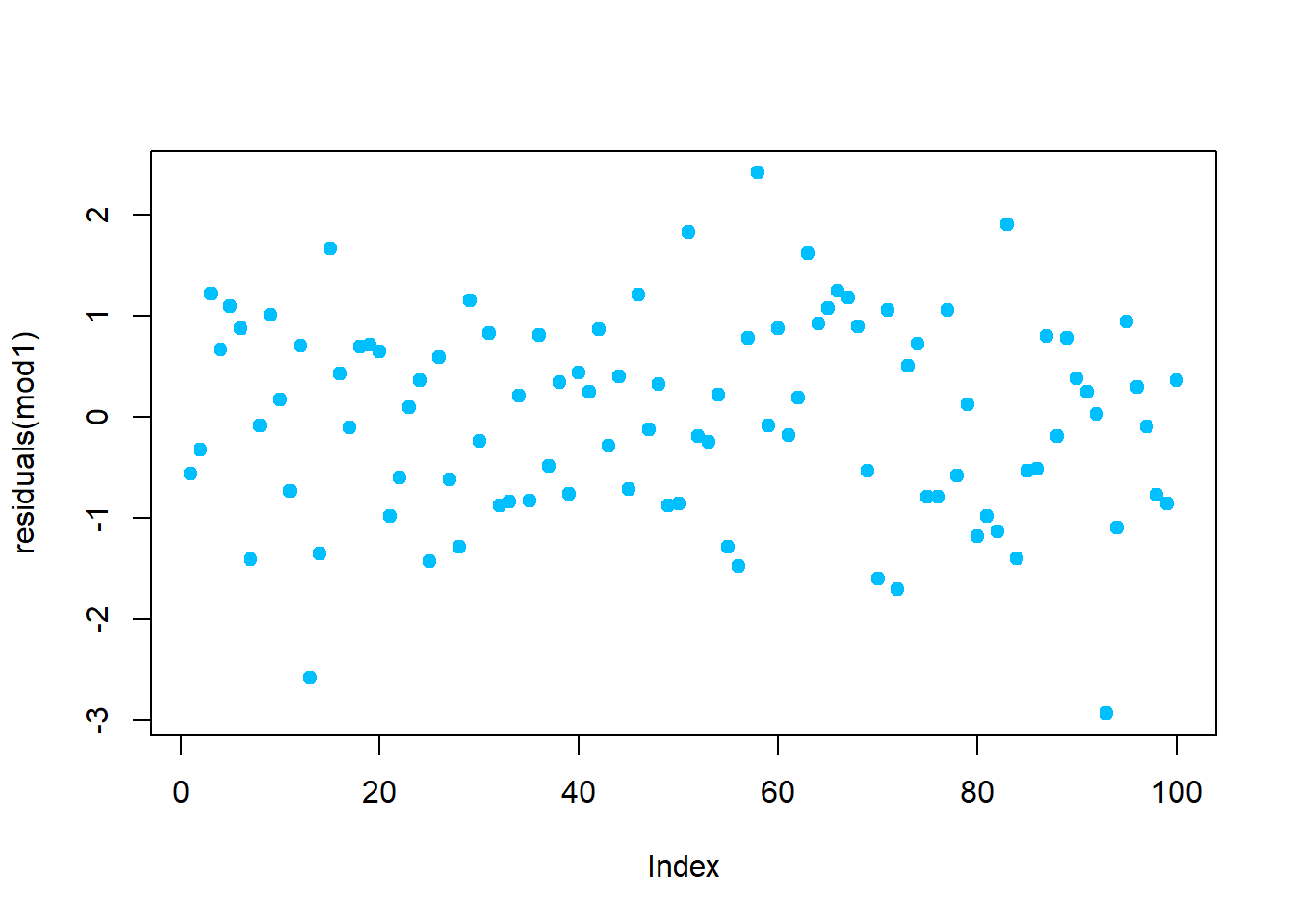
## generate the AR(1) error terms with parameter rho = 0.9 respectively
err2 <- stats::filter(x=err1, filter=0.9, method="recursive")
## generate dependent variable
y2 <- 1 + x + err2
mod2 <- lm(y2 ~ x)
dwtest(mod2) ## perform Durbin-Watson test##
## Durbin-Watson test
##
## data: mod2
## DW = 0.27804, p-value < 2.2e-16
## alternative hypothesis: true autocorrelation is greater than 0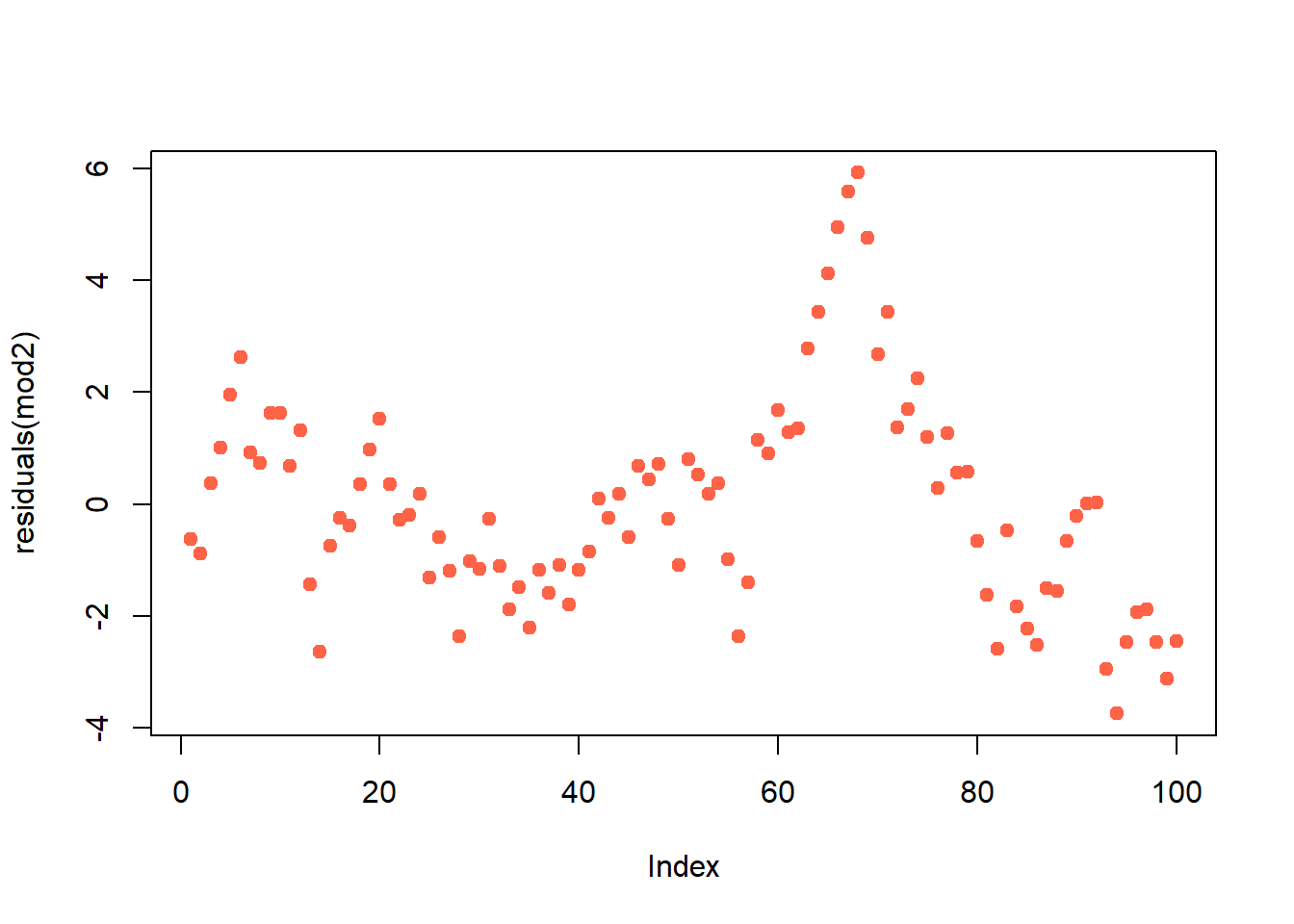
Breusch-Godfrey Test
La función bgtest del paquete lmtest Hothorn et al. (2022) implementa esta prueba.
Ejemplo
Usando los datos el ejemplo anterior aplicar la prueba Breusch-Godfrey.
##
## Breusch-Godfrey test for serial correlation of order up to 1
##
## data: mod1
## LM test = 0.051656, df = 1, p-value = 0.8202##
## Breusch-Godfrey test for serial correlation of order up to 1
##
## data: mod2
## LM test = 73.866, df = 1, p-value < 2.2e-16