These functions define the density, distribution function, quantile function and random generation for the Unit-Power Half-Normal distribution with parameter \(\mu\) and \(\sigma\).
dUPHN(x, mu, sigma, log = FALSE)
pUPHN(q, mu, sigma, lower.tail = TRUE, log.p = FALSE)
qUPHN(p, mu, sigma, lower.tail = TRUE, log.p = FALSE)
rUPHN(n, mu, sigma)Arguments
- x, q
vector of (non-negative integer) quantiles.
- mu
vector of the mu parameter.
- sigma
vector of the sigma parameter.
- log, log.p
logical; if TRUE, probabilities p are given as log(p).
- lower.tail
logical; if TRUE (default), probabilities are \(P[X <= x]\), otherwise, \(P[X > x]\).
- p
vector of probabilities.
- n
number of random values to return.
Details
The Unit-Power Half-Normal distribution with parameters \(\mu\) and \(\sigma\) has a support in \((0, 1)\) and density given by
\(f(x| \mu, \sigma) = \frac{2\mu}{\sigma x^2} \phi(\frac{1-x}{\sigma x}) (2 \Phi(\frac{1-x}{\sigma x})-1)^{\mu-1}\)
for \(0 < x < 1\), \(\mu > 0\) and \(\sigma > 0\).
References
Santoro, K. I., Gómez, Y. M., Soto, D., & Barranco-Chamorro, I. (2024). Unit-Power Half-Normal Distribution Including Quantile Regression with Applications to Medical Data. Axioms, 13(9), 599.
See also
dUPHN.
Examples
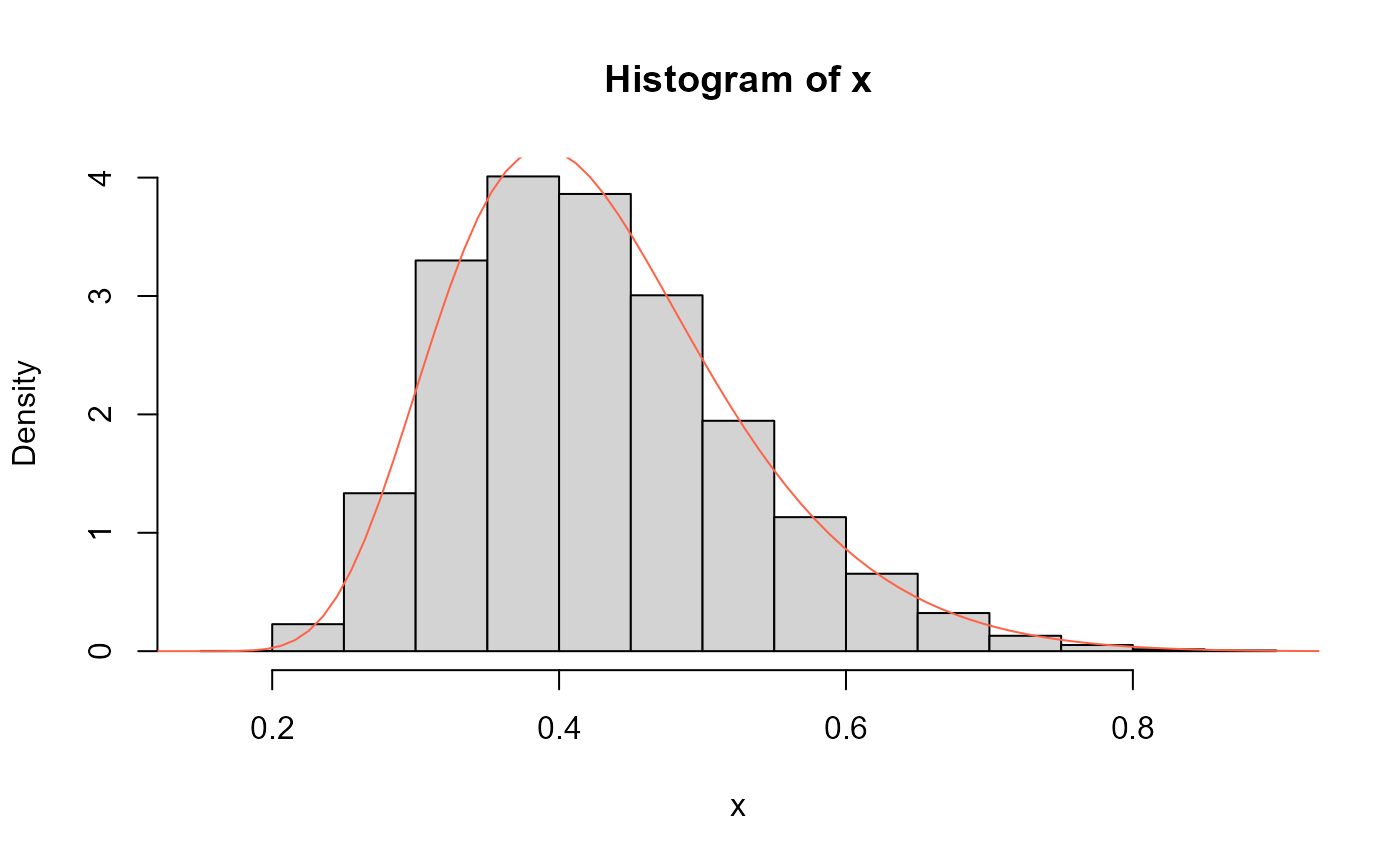
# Example 1
# Plotting the density function for different parameter values
curve(dUPHN(x, mu=1, sigma=1), ylim=c(0, 5),
from=0.01, to=0.99, col="black", las=1, ylab="f(x)")
curve(dUPHN(x, mu=2, sigma=1),
add=TRUE, col= "red")
curve(dUPHN(x, mu=3, sigma=1),
add=TRUE, col="seagreen")
curve(dUPHN(x, mu=4, sigma=1),
add=TRUE, col="royalblue2")
legend("topright", col=c("black", "red", "seagreen", "royalblue2"),
lty=1, bty="n",
legend=c("mu=1, sigma=1",
"mu=2, sigma=1",
"mu=3, sigma=1",
"mu=4, sigma=1"))
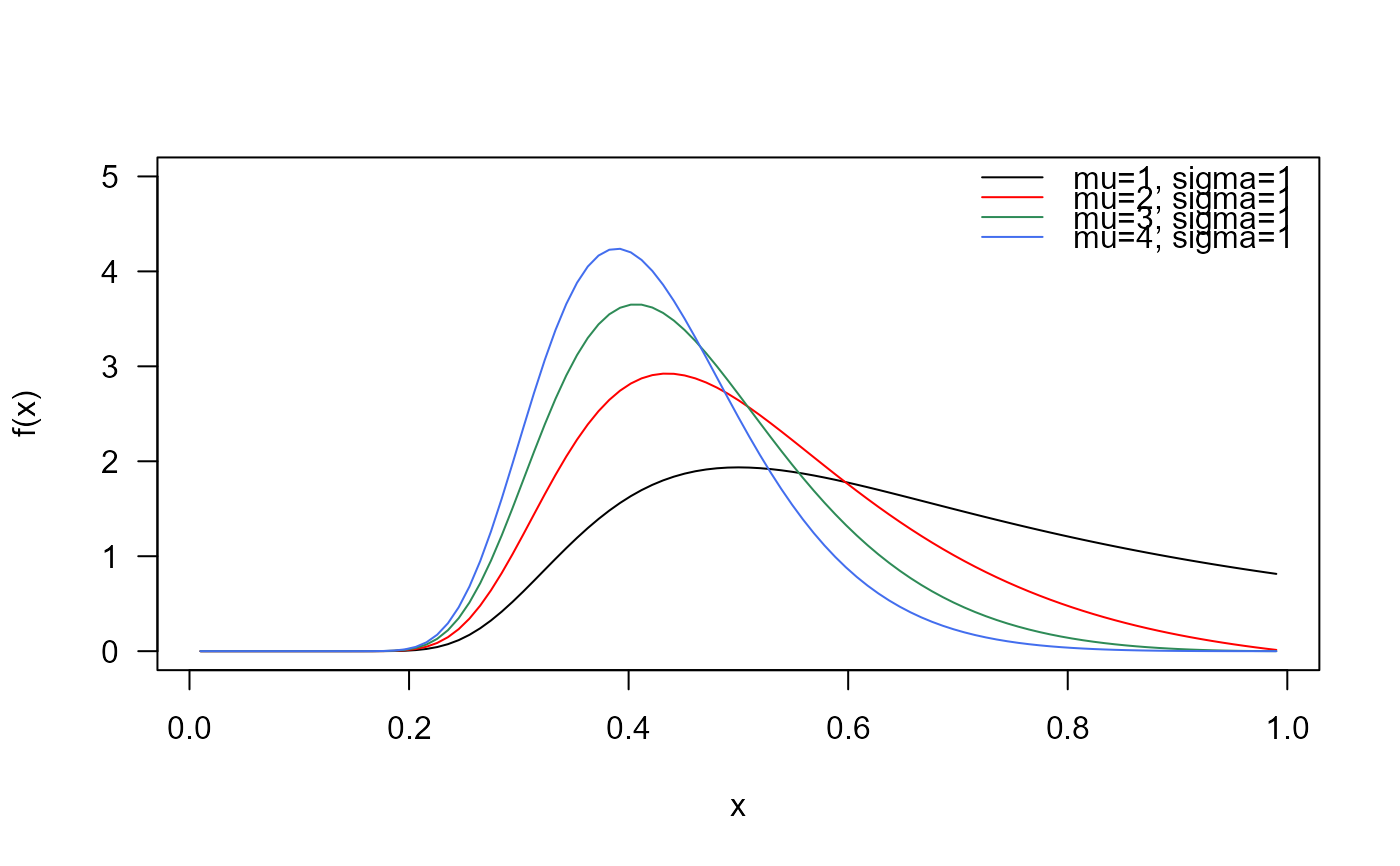 # Example 2
# Checking if the cumulative curves converge to 1
curve(pUPHN(x, mu=1, sigma=1),
from=0.01, to=0.99, col="black", las=1, ylab="F(x)")
curve(pUPHN(x, mu=2, sigma=1),
add=TRUE, col= "red")
curve(pUPHN(x, mu=3, sigma=1),
add=TRUE, col="seagreen")
curve(pUPHN(x, mu=4, sigma=1),
add=TRUE, col="royalblue2")
legend("topleft", col=c("black", "red", "seagreen", "royalblue2"),
lty=1, bty="n",
legend=c("mu=1, sigma=1",
"mu=2, sigma=1",
"mu=3, sigma=1",
"mu=4, sigma=1"))
# Example 2
# Checking if the cumulative curves converge to 1
curve(pUPHN(x, mu=1, sigma=1),
from=0.01, to=0.99, col="black", las=1, ylab="F(x)")
curve(pUPHN(x, mu=2, sigma=1),
add=TRUE, col= "red")
curve(pUPHN(x, mu=3, sigma=1),
add=TRUE, col="seagreen")
curve(pUPHN(x, mu=4, sigma=1),
add=TRUE, col="royalblue2")
legend("topleft", col=c("black", "red", "seagreen", "royalblue2"),
lty=1, bty="n",
legend=c("mu=1, sigma=1",
"mu=2, sigma=1",
"mu=3, sigma=1",
"mu=4, sigma=1"))
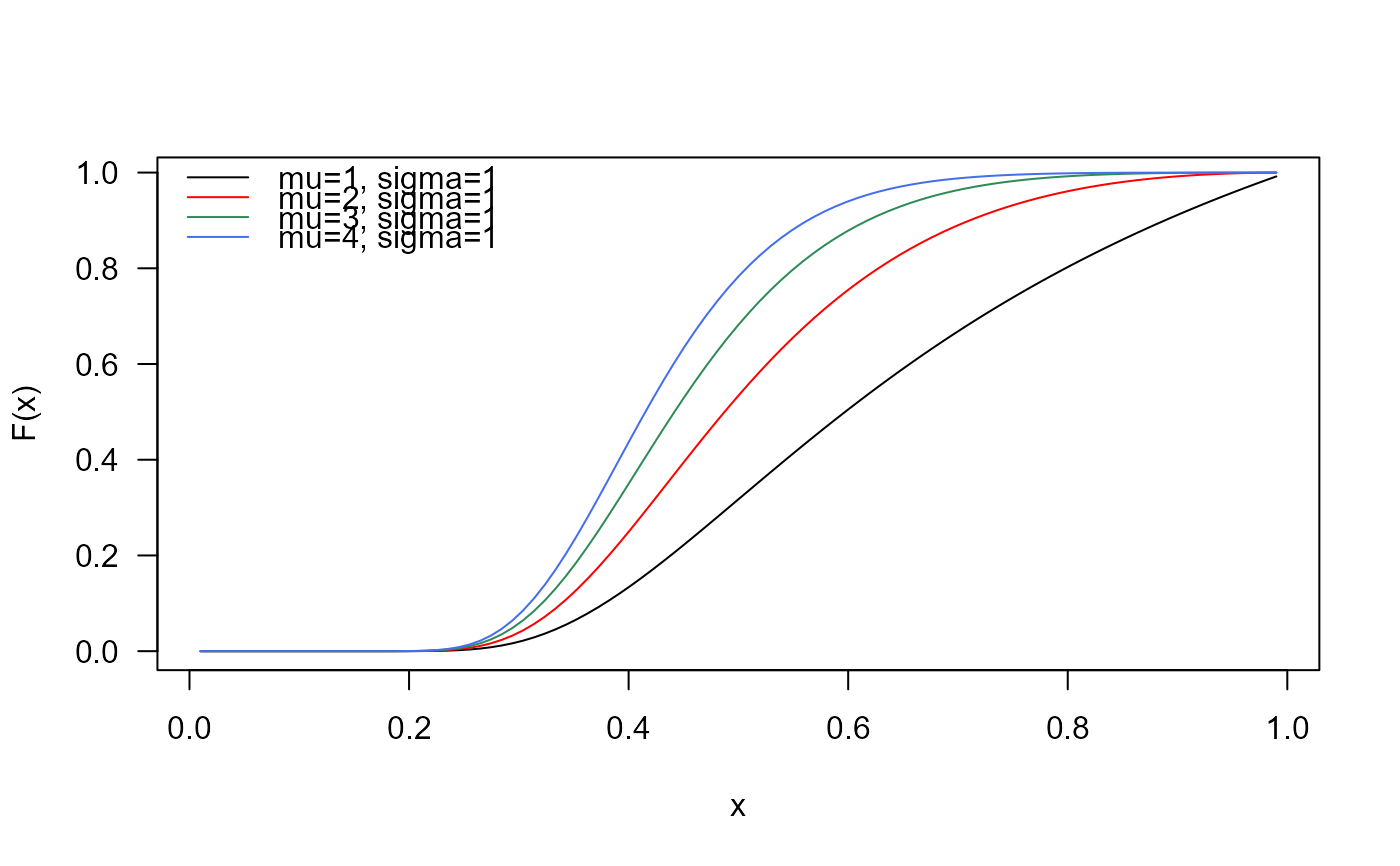 # Example 3
# Checking the quantile function
mu <- 2
sigma <- 3
p <- seq(from=0.01, to=0.99, length.out=100)
plot(x=qUPHN(p, mu=mu, sigma=sigma), y=p,
xlab="Quantile", las=1, ylab="Probability")
curve(pUPHN(x, mu=mu, sigma=sigma), add=TRUE, col="red")
# Example 3
# Checking the quantile function
mu <- 2
sigma <- 3
p <- seq(from=0.01, to=0.99, length.out=100)
plot(x=qUPHN(p, mu=mu, sigma=sigma), y=p,
xlab="Quantile", las=1, ylab="Probability")
curve(pUPHN(x, mu=mu, sigma=sigma), add=TRUE, col="red")
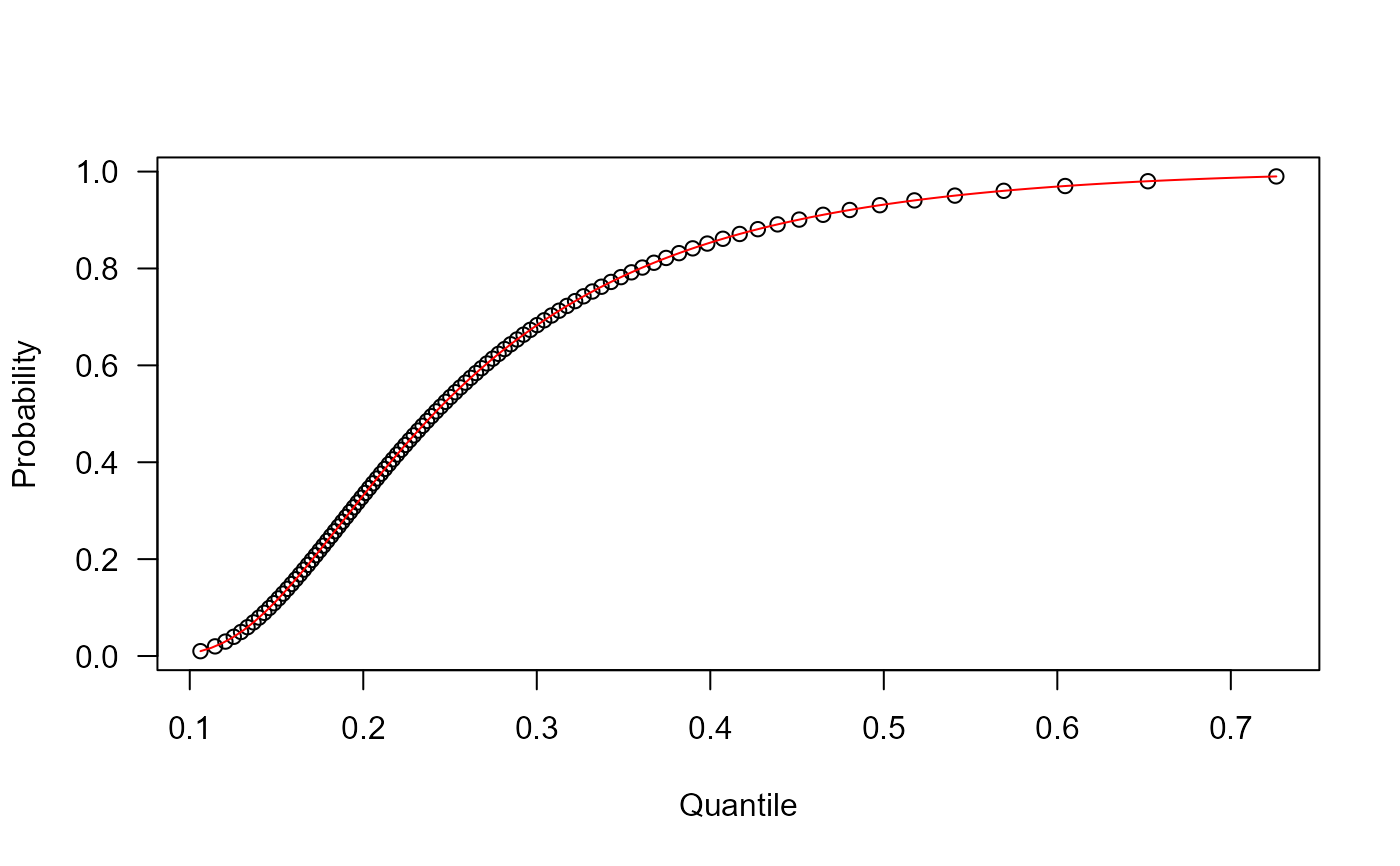 # Example 4
# Comparing the random generator output with
# the theoretical density
x <- rUPHN(n= 10000, mu=4, sigma=1)
hist(x, freq=FALSE)
curve(dUPHN(x, mu=4, sigma=1),
col="tomato", add=TRUE, from=0.01, to=0.99)
# Example 4
# Comparing the random generator output with
# the theoretical density
x <- rUPHN(n= 10000, mu=4, sigma=1)
hist(x, freq=FALSE)
curve(dUPHN(x, mu=4, sigma=1),
col="tomato", add=TRUE, from=0.01, to=0.99)