This function obtains the probability for the Zero Inflated Bivariate Poisson distribution under the parameterization of Lakshminarayana et. al (1993).
dZIBP_Laksh(x, l1, l2, alpha, psi, log = FALSE)
rZIBP_Laksh(n, l1, l2, alpha, psi, max_val_x1 = NULL, max_val_x2 = NULL)Arguments
- x
vector or matrix of quantiles. When
xis a matrix, each row is taken to be a quantile and columns correspond to the number of dimensionsp.- l1
mean for the marginal \(X_1\) variable with Poisson distribution.
- l2
mean for the marginal \(X_2\) variable with Poisson distribution.
- alpha
third parameter.
- psi
parameter with the contamination proportion, \(0 \leq \psi \leq 1\).
- log
logical; if
TRUE, densities d are given as log(d).- n
number of random observations.
- max_val_x1
maximum value for \(X_1\) that is expected, by default it is 100.
- max_val_x2
maximum value for \(X_2\) that is expected, by default it is 100.
Value
Returns the density for a given data x.
References
Lakshminarayana, J., Pandit, S. N., & Srinivasa Rao, K. (1999). On a bivariate Poisson distribution. Communications in Statistics-Theory and Methods, 28(2), 267-276.
Examples
# Example 1 ---------------------------------------------------------------
# Probability for single values of X1 and X2
dZIBP_Laksh(c(0, 0), l1=3, l2=4, alpha=1, psi=0.15)
#> [1] 0.1513813
dZIBP_Laksh(c(1, 0), l1=3, l2=4, alpha=1, psi=0.15)
#> [1] 0.002791271
dZIBP_Laksh(c(0, 1), l1=3, l2=4, alpha=1, psi=0.15)
#> [1] 0.003859537
# Probability for a matrix the values of X1 and X2
x <- matrix(c(0, 0,
1, 0,
0, 1), ncol=2, byrow=TRUE)
x
#> [,1] [,2]
#> [1,] 0 0
#> [2,] 1 0
#> [3,] 0 1
dZIBP_Laksh(x=x, l1=3, l2=4, alpha=1, psi=0.15)
#> [1] 0.151381291 0.002791271 0.003859537
# Checking if the probabilities sum 1
val_x1 <- val_x2 <- 0:50
space <- expand.grid(val_x1, val_x2)
space <- as.matrix(space)
l1 <- 3
l2 <- 4
alpha <- -1.27
psi <- 0.15
probs <- dZIBP_Laksh(x=space, l1=l1, l2=l2, alpha=alpha, psi=psi)
sum(probs)
#> [1] 1
# Example 2 ---------------------------------------------------------------
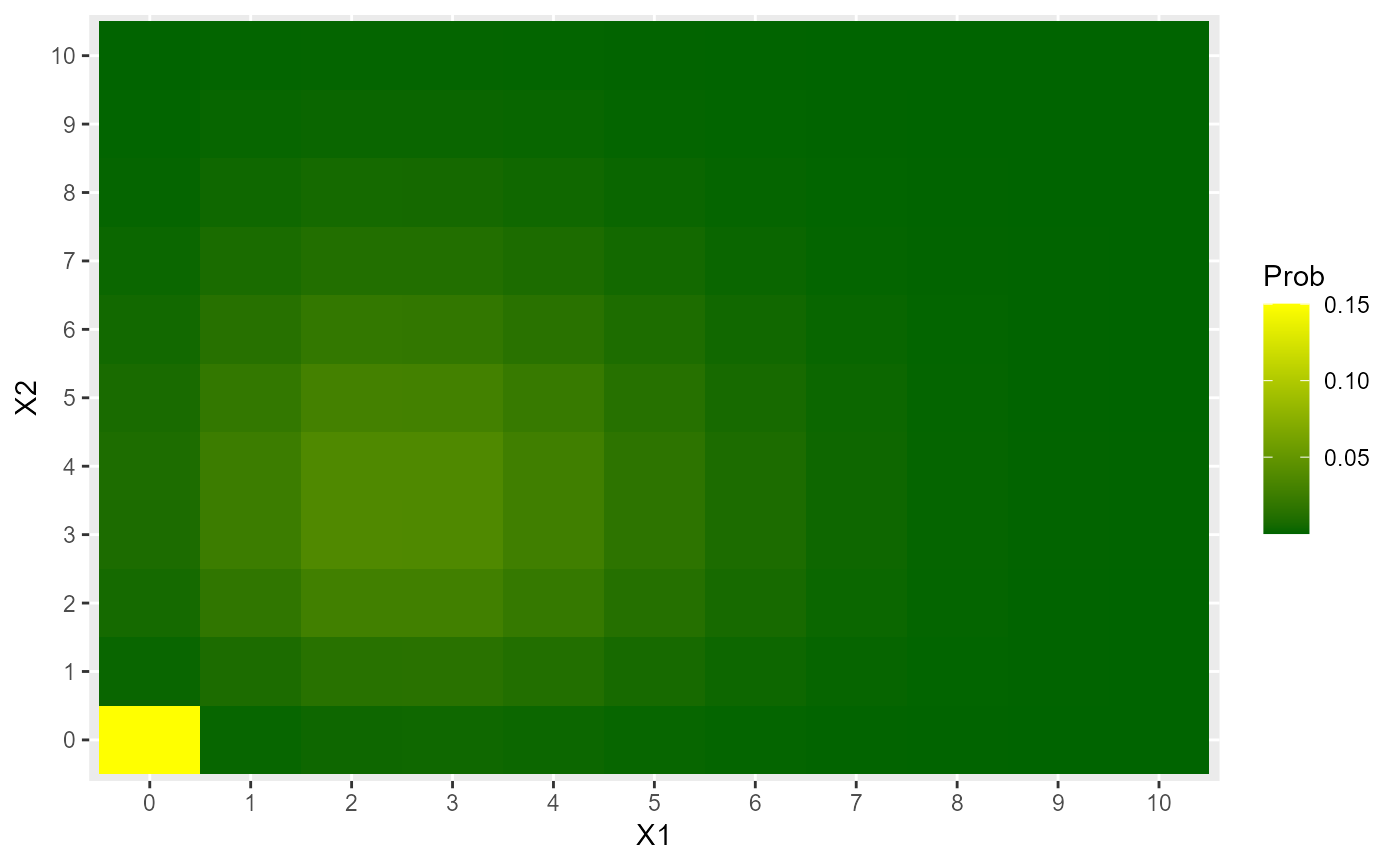
# Heat map for a ZIBP_Laksh
l1 <- 3
l2 <- 4
alpha <- -1.2
psi <- 0.15
X1 <- 0:10
X2 <- 0:10
data <- expand.grid(X1=X1, X2=X2)
data$Prob <- dZIBP_Laksh(x=data, l1=l1, l2=l2, alpha=alpha, psi=psi)
data$X1 <- factor(data$X1)
data$X2 <- factor(data$X2)
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(data, aes(X1, X2, fill=Prob)) +
geom_tile() +
scale_fill_gradient(low="darkgreen", high="yellow")
 # Example 3 ---------------------------------------------------------------
# Generating random values and moment estimations
l1 <- 15
l2 <- 13
correct_alpha_BP_Laksh(l1, l2)
#> $min_alpha
#> [1] -1.000346
#>
#> $max_alpha
#> [1] 1.000346
#>
alpha <- 0.9
psi <- 0.20
x <- rZIBP_Laksh(n=50000, l1, l2, alpha, psi)
moments_estim_ZIBP_Laksh(x)
#> l1_hat l2_hat alpha_hat psi_hat
#> 15.0018 13.0043 -1.0003 0.2004
# Example 4 ---------------------------------------------------------------
# Estimating the parameters using the loglik function
# Loglik function
llZIBP_Laksh <- function(param, x) {
l1 <- param[1] # param: is the parameter vector
l2 <- param[2]
alpha <- param[3]
psi <- param[4]
sum(dZIBP_Laksh(x=x, l1=l1, l2=l2,
alpha=alpha, psi=psi, log=TRUE))
}
# The known parameters
l1 <- 5
l2 <- 3
correct_alpha_BP_Laksh(l1=l1, l2=l2)
#> $min_alpha
#> [1] -1.228726
#>
#> $max_alpha
#> [1] 1.228726
#>
alpha <- -1.20
psi <- 0.20
set.seed(12345)
x <- rZIBP_Laksh(n=500, l1=l1, l2=l2, alpha=alpha, psi=psi)
# To obtain reasonable values for alpha
theta <- as.numeric(moments_estim_ZIBP_Laksh(x))
theta
#> [1] 5.1505 2.8738 -1.2420 0.1760
# To create start parameters
min_alpha <- correct_alpha_BP_Laksh(l1=theta[1],
l2=theta[2])$min_alpha
max_alpha <- correct_alpha_BP_Laksh(l1=theta[1],
l2=theta[2])$max_alpha
start_param <- theta
names(start_param) <- c("l1_hat", "l2_hat", "alpha_hat", "psi_hat")
start_param
#> l1_hat l2_hat alpha_hat psi_hat
#> 5.1505 2.8738 -1.2420 0.1760
# Estimating parameters
res1 <- optim(fn = llZIBP_Laksh,
par = start_param,
lower = c(0.001, 0.001, min_alpha, 0.0001),
upper = c( Inf, Inf, max_alpha, 0.9999),
method = "L-BFGS-B",
control = list(maxit=100000, fnscale=-1),
x=x)
res1
#> $par
#> l1_hat l2_hat alpha_hat psi_hat
#> 5.1490422 2.8716417 -1.2420012 0.1759906
#>
#> $value
#> [1] -1960.879
#>
#> $counts
#> function gradient
#> 6 6
#>
#> $convergence
#> [1] 0
#>
#> $message
#> [1] "CONVERGENCE: REL_REDUCTION_OF_F <= FACTR*EPSMCH"
#>
# Example 3 ---------------------------------------------------------------
# Generating random values and moment estimations
l1 <- 15
l2 <- 13
correct_alpha_BP_Laksh(l1, l2)
#> $min_alpha
#> [1] -1.000346
#>
#> $max_alpha
#> [1] 1.000346
#>
alpha <- 0.9
psi <- 0.20
x <- rZIBP_Laksh(n=50000, l1, l2, alpha, psi)
moments_estim_ZIBP_Laksh(x)
#> l1_hat l2_hat alpha_hat psi_hat
#> 15.0018 13.0043 -1.0003 0.2004
# Example 4 ---------------------------------------------------------------
# Estimating the parameters using the loglik function
# Loglik function
llZIBP_Laksh <- function(param, x) {
l1 <- param[1] # param: is the parameter vector
l2 <- param[2]
alpha <- param[3]
psi <- param[4]
sum(dZIBP_Laksh(x=x, l1=l1, l2=l2,
alpha=alpha, psi=psi, log=TRUE))
}
# The known parameters
l1 <- 5
l2 <- 3
correct_alpha_BP_Laksh(l1=l1, l2=l2)
#> $min_alpha
#> [1] -1.228726
#>
#> $max_alpha
#> [1] 1.228726
#>
alpha <- -1.20
psi <- 0.20
set.seed(12345)
x <- rZIBP_Laksh(n=500, l1=l1, l2=l2, alpha=alpha, psi=psi)
# To obtain reasonable values for alpha
theta <- as.numeric(moments_estim_ZIBP_Laksh(x))
theta
#> [1] 5.1505 2.8738 -1.2420 0.1760
# To create start parameters
min_alpha <- correct_alpha_BP_Laksh(l1=theta[1],
l2=theta[2])$min_alpha
max_alpha <- correct_alpha_BP_Laksh(l1=theta[1],
l2=theta[2])$max_alpha
start_param <- theta
names(start_param) <- c("l1_hat", "l2_hat", "alpha_hat", "psi_hat")
start_param
#> l1_hat l2_hat alpha_hat psi_hat
#> 5.1505 2.8738 -1.2420 0.1760
# Estimating parameters
res1 <- optim(fn = llZIBP_Laksh,
par = start_param,
lower = c(0.001, 0.001, min_alpha, 0.0001),
upper = c( Inf, Inf, max_alpha, 0.9999),
method = "L-BFGS-B",
control = list(maxit=100000, fnscale=-1),
x=x)
res1
#> $par
#> l1_hat l2_hat alpha_hat psi_hat
#> 5.1490422 2.8716417 -1.2420012 0.1759906
#>
#> $value
#> [1] -1960.879
#>
#> $counts
#> function gradient
#> 6 6
#>
#> $convergence
#> [1] 0
#>
#> $message
#> [1] "CONVERGENCE: REL_REDUCTION_OF_F <= FACTR*EPSMCH"
#>